Introduction
Ever wondered what makes your cakes and muffins light and fluffy? Monocalcium phosphate (MCP) could be the secret ingredient. This compound is widely used in food production for its ability to help food rise and maintain quality.
In this article, we'll explore the role of MCP in food, how it works, and the various products it enhances. You’ll learn about its uses in baking, processed foods, and more.
What is Monocalcium Phosphate?
Monocalcium phosphate is a chemical compound with the formula Ca(H2PO4)2. It contains both calcium and phosphorus, two essential minerals required for various biological functions. The compound exists in two main forms: monohydrate (MCP-M), which contains water, and anhydrous (MCP-A), which lacks water. These two forms of MCP have different uses depending on their physical properties.
Monocalcium phosphate is commonly used in the food industry for its ability to act as a leavening agent. When combined with a base like sodium bicarbonate, it releases carbon dioxide gas, which causes dough to rise. This process is essential in baking, where the goal is to achieve a light, fluffy texture in products such as cakes, muffins, and breads.
Form | Description | Common Use |
Monohydrate (MCP-M) | Contains one water molecule. | Fast-acting in baked goods |
Anhydrous (MCP-A) | Does not contain water. | Slower reaction in baking mixes |
How Does Monocalcium Phosphate Work in Food?
Leavening Agent
One of the most important functions of monocalcium phosphate in food is its role as a leavening agent. Leavening agents are substances that cause the dough or batter to rise by producing gas. MCP works in conjunction with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) to release carbon dioxide when they react. The carbon dioxide bubbles expand within the dough or batter, causing the mixture to rise and creating the light, airy texture that is characteristic of many baked goods. This reaction is fast-acting, making MCP an ideal choice for recipes that require immediate leavening.
Dough Conditioner
Apart from its role in leavening, monocalcium phosphate also acts as a dough conditioner. In bakery products, it improves the consistency and texture of the dough, resulting in a product that is soft yet structurally stable. It enhances the handling properties of dough, making it easier to shape and manipulate during processing. Additionally, MCP helps extend the shelf life of baked goods by maintaining moisture and preventing dryness, which can lead to spoilage.
Acidulant and Buffer
Monocalcium phosphate also functions as an acidulant in food. An acidulant is a substance that helps regulate the acidity of a food product. In processed foods like beverages, salad dressings, and processed cheeses, MCP helps maintain the desired pH levels, which is crucial for both flavor and stability. The ability of MCP to buffer and control acidity is especially important in maintaining the quality of foods that are stored for long periods or subjected to varying temperatures.
Applications of Monocalcium Phosphate in Food Products
Monocalcium phosphate is a common ingredient in many food products. Its unique properties make it an indispensable component in the food manufacturing industry.
In Bakery Products
The most prominent application of monocalcium phosphate is in the baking industry. It is an essential ingredient in baking powders, where it is combined with other leavening agents like sodium bicarbonate to create the necessary chemical reaction for rising. Foods such as cakes, muffins, pancakes, and biscuits rely on MCP for the light, fluffy texture that consumers expect. The precise control of the leavening process is crucial in producing consistent, high-quality bakery products.
In Processed Foods
Monocalcium phosphate is also used in a variety of processed foods. It acts as a stabilizer, helping to maintain the texture and moisture content of products like canned vegetables, instant puddings, and ready-to-eat meals. In these products, MCP prevents caking and ensures that the ingredients remain evenly distributed. Its ability to retain moisture helps to keep the product fresh for longer, extending its shelf life.
In Beverages and Supplements
In addition to its role in solid foods, monocalcium phosphate is also used in the beverage industry. It is commonly found in energy drinks and other powdered beverages, where it serves as a calcium source. As a supplement, it helps fortify drinks with essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are important for bone health and overall well-being, which makes MCP an important component in products aimed at enhancing nutrition.
Food Category | Products Containing MCP | Function |
Bakery Products | Cakes, Muffins, Pancakes, Breads | Leavening agent, dough conditioner |
Processed Foods | Instant Puddings, Canned Vegetables, Convenience Foods | Prevents caking, improves texture |
Beverages | Energy Drinks, Powdered Beverages | Fortification (calcium source) |
Supplements | Nutritional Supplements | Calcium and phosphorus source |
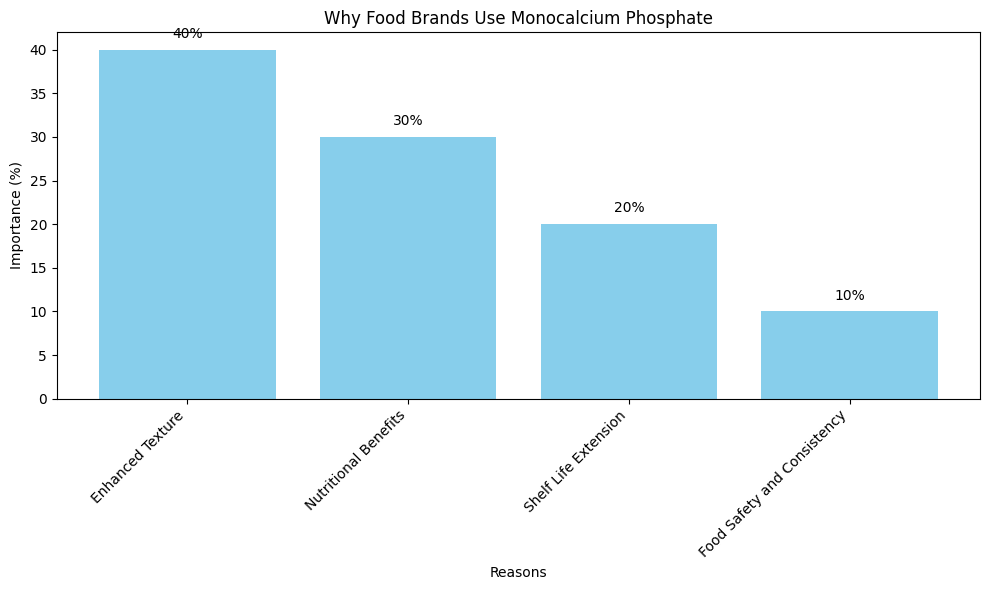
Why Do Food Brands Use Monocalcium Phosphate?
Food manufacturers increasingly rely on monocalcium phosphate (MCP) due to its versatility and the various benefits it offers in food production. Its multifunctionality as a leavening agent, acidulant, and dough conditioner makes it essential for creating high-quality products. Below are the main reasons food brands choose MCP for their formulations:
Enhanced Texture
MCP significantly improves the texture of baked goods by contributing to their lightness and fluffiness. By helping to create a uniform grain and rise, it ensures that cakes, muffins, and other baked products have the desired softness and airiness. The controlled gas release from MCP in combination with other leavening agents allows for a perfectly balanced product.
Nutritional Benefits
Monocalcium phosphate is a rich source of calcium and phosphorus, both of which are crucial minerals for human health. These nutrients are vital for maintaining strong bones and teeth, as well as supporting various metabolic functions in the body. Food brands fortify their products with MCP to enhance their nutritional profile, providing consumers with added health benefits, particularly in fortified foods and dietary supplements.
Shelf Life Extension
One of the key benefits of MCP is its ability to improve moisture retention in food. This feature helps extend the shelf life of many products, from baked goods to processed foods. By preventing the drying out or caking of ingredients, MCP ensures that products remain fresh and of high quality for a longer period, reducing waste and increasing consumer satisfaction.
Incorporating MCP into food products enables manufacturers to deliver better texture, nutritional value, and prolonged freshness—all while adhering to global safety standards. This makes MCP a vital ingredient in creating high-quality food that consumers trust.
Type of Phosphate | Monocalcium Phosphate | Dicalcium Phosphate | Tricalcium Phosphate |
Chemical Composition | Ca(H2PO4)2 | CaHPO4 | Ca3(PO4)2 |
Primary Use | Leavening agent, acidulant, calcium & phosphorus source | Animal feed, nutritional supplement | Calcium supplement, anticaking agent |
Solubility | Moderately soluble in water | Slightly soluble in water | Insoluble in water |
Health and Safety Considerations
Monocalcium phosphate has been extensively tested and is considered safe for consumption by regulatory bodies worldwide. In the United States, it is classified as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) by the FDA, which means that experts have determined it poses no significant risk to health when used appropriately. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated its safety, confirming that MCP is safe for use in food products.
However, as with all food additives, it is important to consume monocalcium phosphate in moderation. Excessive intake of phosphorus, which MCP provides, can have negative health effects, such as disrupting calcium balance and potentially contributing to kidney or heart problems. Therefore, it is essential to follow regulatory guidelines for MCP usage in food products to ensure safety.
Conclusion
Monocalcium phosphate is essential in the food industry, especially in baking. It acts as a leavening agent, dough conditioner, and acidulant, improving texture, flavor, and nutrition. From baked goods to processed foods, MCP enhances everyday food products. With its safety confirmed by global authorities, it remains a key ingredient in food production, adding both functional and nutritional value.
Aurora Industry Co., Ltd. offers high-quality MCP that supports the food manufacturing process, ensuring superior product quality.
FAQ
Q: What is monocalcium phosphate in food?
A: Monocalcium phosphate (MCP) is a chemical compound used in food as a leavening agent, acidulant, and dough conditioner. It helps baked goods rise and improves texture.
Q: How does monocalcium phosphate work in baking?
A: When combined with baking soda, monocalcium phosphate releases carbon dioxide, causing dough to rise and giving baked goods a light, fluffy texture.
Q: Is monocalcium phosphate safe in food?
A: Yes, monocalcium phosphate is considered safe for consumption and is approved by global regulatory bodies like the FDA and EFSA.
Q: What foods contain monocalcium phosphate?
A: Monocalcium phosphate is commonly found in baking powders, pancakes, cakes, muffins, and other baked goods. It is also used in processed foods and beverages.
Q: How does monocalcium phosphate affect the taste of food?
A: While it is primarily used as a leavening agent, MCP can also affect the flavor by maintaining the acidity in processed foods like beverages and dressings.
Q: Can monocalcium phosphate be used in all food products?
A: Monocalcium phosphate is widely used in baked goods, beverages, and processed foods but is not typically used in raw or unprocessed foods.











