Introduction
Sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP) is a widely used compound in industries like food processing, water treatment, and manufacturing. The main concern is whether SHMP is safe for consumption and use in products. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies, some safety concerns exist, especially regarding long-term use. In this article, we will discuss SHMP’s safety, applications, potential risks, and relevant regulations.
What Is Sodium Hexametaphosphate?
Sodium hexametaphosphate is an inorganic polyphosphate with the chemical formula Na₆[(PO₃)₆]. It is typically found as a white powder or crystalline solid and is highly soluble in water. This compound is created by heating monosodium orthophosphate, which then undergoes polymerization to form a cyclic structure of sodium phosphate units. Sodium hexametaphosphate is used across several industries:
● Food Industry: It serves as a sequestrant, emulsifier, and texturizer in various food products such as cheese powders, canned beverages, and processed meats.
● Water Treatment: SHMP is effective as a dispersing agent in water treatment to prevent scale buildup in pipes and boilers.
● Other Industries: It also finds applications in ceramics, detergents, and even in pet foods to prevent tartar buildup in animals.
While SHMP plays a crucial role in improving food quality, water treatment, and industrial processes, its safety has been questioned due to potential side effects when consumed in large quantities.
Industry | Application |
Food Industry | Sequestrant, emulsifier, and texturizer in food products |
Water Treatment | Dispersing agent to prevent scale buildup in pipes and boilers |
Other Industries | Used in ceramics, detergents, and pet foods |
Is Sodium Hexametaphosphate Safe for Consumption?
The safety of sodium hexametaphosphate, especially in food products, is a significant concern. Regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), have classified SHMP as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used within specified limits. The GRAS designation means that, based on scientific evidence, SHMP is considered safe for human consumption under normal usage conditions.
However, like many substances, sodium hexametaphosphate can pose risks when consumed in excessive amounts. High phosphate intake is known to interfere with calcium absorption in the body, potentially leading to health issues like weakened bones, kidney problems, and cardiovascular concerns, particularly in individuals with pre-existing conditions such as kidney disease. This is because SHMP, like other phosphate compounds, breaks down into phosphate ions in the body, which can lead to elevated phosphate levels.
● Cardiovascular Health: Studies suggest that excessive phosphate levels in the body may contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease, particularly among individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is important to note that these health concerns arise from excessive or chronic consumption, not from the levels typically found in regulated food products.
● Kidney Health: For people with kidney problems, the body’s ability to excrete excess phosphates is reduced, which can lead to complications like kidney stones and further deterioration of kidney function.
Safety Concerns and Side Effects of Sodium Hexametaphosphate
Despite sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP) being considered safe for general consumption, it is essential to recognize the potential side effects, particularly when consumed in large quantities or over extended periods. While the compound is widely used and regulated, any substance has the potential to cause adverse effects when not used properly.
Short-Term Side Effects
● Gastrointestinal Irritation: Sodium hexametaphosphate can irritate the digestive system, particularly when consumed in large amounts. Individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal discomfort. This can occur due to the compound's ability to affect the pH balance in the gastrointestinal tract, leading to disturbances in digestion.
● Headaches and Dizziness: Some individuals may experience headaches or dizziness, potentially due to a disruption in the body's electrolyte balance. Phosphates like SHMP play a role in fluid regulation, and in sensitive individuals, an imbalance may lead to these symptoms.
● Allergic Reactions: Although rare, there have been reports of allergic reactions to sodium hexametaphosphate. Symptoms can range from mild skin rashes and itching to more severe reactions, such as swelling of the face or throat and difficulty breathing. Those with known sensitivities to similar compounds should avoid exposure or consult a healthcare provider.
Long-Term Side Effects
● Impact on Bone Health: Long-term exposure to elevated phosphate levels, including those from SHMP, could disrupt calcium absorption and balance in the body. This disruption can lead to a higher risk of bone loss, osteoporosis, and fractures, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly or individuals with already compromised bone health.
● Kidney Damage: Excessive phosphate intake over time may cause damage to the kidneys, particularly for individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions. The kidneys are responsible for eliminating excess phosphate from the body, and when phosphate levels exceed the kidneys' ability to process them, it could lead to kidney strain and long-term damage.
● Potential for Toxicity: Some studies indicate that high concentrations of sodium hexametaphosphate could potentially cause oxidative stress and cellular damage in specific tissues. While this may not reflect normal usage, the risk of toxicity with prolonged exposure to very high doses remains a concern. Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of SHMP at high concentrations.
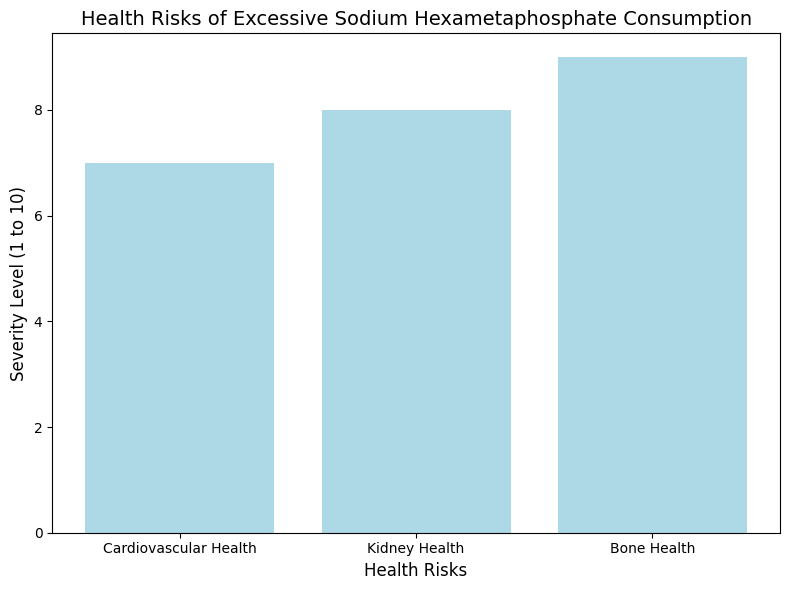
Health Risk | Effect |
Cardiovascular Health | Elevated phosphate levels can contribute to cardiovascular issues, especially in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD). |
Kidney Health | Excessive phosphate intake can lead to kidney strain and damage, particularly in individuals with kidney problems. |
Bone Health | Disruption of calcium absorption may lead to bone loss, osteoporosis, and fractures. |
Safety of Sodium Hexametaphosphate in Pet Products
Sodium hexametaphosphate is also commonly used in pet products, especially in dental care items for dogs. Its primary function in pet food is to prevent tartar buildup and promote oral health. While it provides benefits in maintaining a pet's oral hygiene, concerns about the safety of SHMP for pets, especially with long-term or excessive exposure, are also important.
Oral Health Benefits:
When used in controlled amounts, SHMP has significant benefits for pet oral health. It helps in preventing tartar buildup, maintaining a clean mouth, and promoting better overall dental hygiene for pets. This is particularly useful in preventing periodontal disease, which is common in dogs.
Potential Risks:
While SHMP offers oral health benefits, excessive levels can lead to gastrointestinal issues in pets, including upset stomach, vomiting, and diarrhea. Prolonged exposure to high amounts could also stress a pet's kidneys and liver, leading to potential organ damage over time. Pet owners must ensure that the amount of SHMP in pet foods is compliant with safety standards to prevent overexposure.
Precautions for Pet Owners:
Pet owners should carefully monitor the amount of SHMP present in their pet's food and ensure that they purchase products that comply with safety guidelines. If pets show any signs of digestive issues, changes in behavior, or loss of appetite, it is advisable to consult with a veterinarian. Additionally, pet owners should not solely rely on pet food for dental health but should incorporate regular oral hygiene practices, such as brushing their pet's teeth, to reduce the risk of tartar buildup.
Environmental and Ecological Impact of Sodium Hexametaphosphate
The use of sodium hexametaphosphate also raises environmental concerns, particularly in water treatment and agricultural settings. As a chemical compound that is highly soluble in water, SHMP can have significant effects on the environment if not properly managed.
● Water Quality and Eutrophication: Sodium hexametaphosphate, when released into the environment, can contribute to eutrophication in water bodies. Eutrophication is the overgrowth of algae and aquatic plants, which depletes oxygen in the water, leading to the death of aquatic life. This can affect both freshwater and marine ecosystems.
● Soil Impact: The high phosphorus content in SHMP can also disrupt the nutrient balance in soils. Excess phosphorus can interfere with the availability of other essential nutrients, like iron and zinc, which are vital for plant growth. This imbalance can harm crop yields and affect agricultural productivity.
Global Regulations and Safety Standards for Sodium Hexametaphosphate
Sodium hexametaphosphate is regulated by several global agencies to ensure its safety for both human consumption and environmental impact.
● FDA (United States): SHMP is classified as GRAS for use in food products under specific limits. This ensures that it is safe for consumption when used according to established guidelines.
● EFSA (European Union): The EFSA has also reviewed SHMP and established acceptable daily intake levels for phosphate additives, including SHMP. These levels are designed to ensure consumer safety and limit potential risks from overexposure.
● Other Regions: Regulatory bodies in countries like Canada, Japan, and China have set similar standards for SHMP use in food and other products, based on extensive scientific research.
These regulatory measures ensure that sodium hexametaphosphate is used safely in food, water treatment, and industrial processes while minimizing potential risks to human health and the environment.
Conclusion
Sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP) is generally safe when used within regulated limits in food products, water treatment, and industrial applications. It enhances food quality, promotes pet oral health, and aids in water treatment. However, excessive exposure can lead to health risks, such as calcium absorption issues, kidney damage, and cardiovascular concerns. Both consumers and industries must follow safety regulations to minimize risks. Aurora Industry Co., Ltd. ensures the production of high-quality SHMP, providing valuable solutions across various applications.
FAQ
Q: What is sodium hexametaphosphate?
A: Sodium hexametaphosphate is a polyphosphate compound used as a sequestrant, emulsifier, and texturizer in industries like food processing and water treatment.
Q: Is sodium hexametaphosphate safe for consumption?
A: Yes, sodium hexametaphosphate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA when used in regulated amounts in food products.
Q: What are the health risks of sodium hexametaphosphate?
A: Excessive consumption of sodium hexametaphosphate may lead to calcium absorption issues, kidney function disruption, and cardiovascular concerns.
Q: Can sodium hexametaphosphate be harmful to pets?
A: Sodium hexametaphosphate is safe for pets in controlled amounts, especially for oral health, but excessive exposure can cause gastrointestinal irritation and organ stress.
Q: What is the role of sodium hexametaphosphate in food products?
A: Sodium hexametaphosphate is used to improve texture, prevent discoloration, and preserve the quality of food, especially in processed meats, dairy, and beverages.
Q: What environmental concerns are associated with sodium hexametaphosphate?
A: High levels of sodium hexametaphosphate in water can contribute to eutrophication, leading to algae growth and negatively affecting aquatic ecosystems.











